|
Roman Empire Timeline and Roman Invasion of Britain
|
|
Period:
The Monarchy, 753 BC to 509 BC |
|||
|
Political
and military events |
Cultural
and other events |
||
| 753 | Foundation of Rome | ||
| 616-579 |  Tarquinius
Priscus Tarquinius
Priscus |
c.600 |
Earliest Latin inscriptions Capitoline temple built |
| 579-543 |  Servius
Tullius Servius
Tullius |
||
|
543-509 |
 Tarquinius
Superbus Tarquinius
Superbus |
||
| 509 | Expulsion of the Kings | More temples built | |
| 494 |  Plebeians
struggle with patricians for rights Plebeians
struggle with patricians for rights |
First law code: Twelve Tables | |
| 450 | City wall built Romanisation of Italy | ||
| 390 |  Rome
sacked by Gauls Rome
sacked by Gauls |
||
| 378 |  Appian
Way built Appian
Way built |
||
| 338 | Extension of Roman citizenship | 312 | Coinage begins |
| 278 |  End
of struggle with patricians End
of struggle with patricians |
c280 |  First
gladiatorial games First
gladiatorial games |
| 272 | Rome wins control of whole of Italy | Hellenisation of Roman society; comedies of Plautus and Terence; poetry of Ennius | |
| 264-241 | 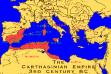 First
Punic War (against Carthage): Rome wins Sicily First
Punic War (against Carthage): Rome wins Sicily |
||
| 218-201 |  Second
Punic War: Hannibal defeated; 206 Spain becomes two Roman provinces Second
Punic War: Hannibal defeated; 206 Spain becomes two Roman provinces |
||
| 214-167 |  Macedonian
Wars Macedonian
Wars |
||
| 197-133 | Wars in Spain | ||
| 149-146 | 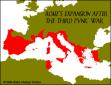 Third
Punic War: Carthage destroyed, Africa becomes Roman province Third
Punic War: Carthage destroyed, Africa becomes Roman province |
||
| 148 | 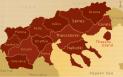 Macedonia
becomes Roman province Macedonia
becomes Roman province |
||
| 133 |  Asia
becomes Roman province; land reforms of Tiberius Gracchus Asia
becomes Roman province; land reforms of Tiberius Gracchus |
  |
|
| 123-122 |
|
  |
|
| 113-101 |  War
against Cimbri War
against Cimbri |
||
| 107-86 |  Seven
consulships of Marius; 104 army reform Seven
consulships of Marius; 104 army reform |
||
| 91-87 | Social War; Roman citizenship extended to all Italy | ||
| 88-85 |  First
Mithridatic War First
Mithridatic War |
||
| 82-81 |  Dictatorship
of Sulla: proscriptions, reforms; rise of Pompey Dictatorship
of Sulla: proscriptions, reforms; rise of Pompey |
||
| 73-71 |  Revolt
of Spartacus Revolt
of Spartacus |
||
| 73-63 |
 Third
Mithridatic War Third
Mithridatic War |
  |
|
| 63 |  Consulship
of Cicero; conspiracy of Catiline Consulship
of Cicero; conspiracy of Catiline |
||
| 60 | 'First triumvirate' (Pompey, Caesar, Crassus) | ||
| 58-50 |  Caesar
conquers Gaul; 55, 54 expeditions to Britain Caesar
conquers Gaul; 55, 54 expeditions to Britain |
|
|
| 49-45 |  Caesar
wins civil war against Pompey and republicans Caesar
wins civil war against Pompey and republicans
|
||
| 44 |  Caesar
dictator for life; assassinated Caesar
dictator for life; assassinated |
46 |  Caesar's
forum Caesar's
forum |
| 43 |   'Second
triumvirate' (Antony, Octavian, Lepidus); proscriptions, murder
of Cicero 'Second
triumvirate' (Antony, Octavian, Lepidus); proscriptions, murder
of Cicero |
c39 |  Histories
of Sallust Histories
of SallustVirgil's Eclogues |
| 32-31 |   Octavian
wins civil war against Mark Antony; 31 Actium Octavian
wins civil war against Mark Antony; 31 Actium |
 |
|
 |
29 | Virgil's Georgics | |
|
Period:
The Empire, 27 BC to AD 476
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Political
and military events
|
Cultural
and other events
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 27 |  Octavian
becomes first emperor Augustus Octavian
becomes first emperor Augustus |
27 |  Agrippa's
Pantheon Agrippa's
Pantheon |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 19 |  Virgil's
Aeneid; poetry of Horace, Tibullus, Propertius, Ovid; history of Livy Virgil's
Aeneid; poetry of Horace, Tibullus, Propertius, Ovid; history of Livy
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 16-AD 6 | Conquest of Danube provinces |
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
13 |
 Theatre
of Marcellus Theatre
of Marcellus |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 9 |
 Ara
Pacis Augustae Ara
Pacis Augustae |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
2 |
 Augustus'
forum Augustus'
forum |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| AD | AD | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 9 |  Varian
disaster Varian
disaster |
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 14 |  Death
of Augustus Death
of Augustus |
14 |
Teaching and death of Christ |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 14-37 |  Tiberius Tiberius
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 37-41 | Caligula
 |
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 41-54 | Claudius |
   |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 43 |  Conquest
of Britain Conquest
of Britain |
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 54-68 |  Nero Nero
|
Treatises and tragedies of Seneca; poetry of Persius and Lucan; novel of Petronius | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 60-61 |
 Boudicca's
revolt Boudicca's
revolt |
64 |  Fire
of Rome; first persecution of Christians Fire
of Rome; first persecution of Christians |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 66-70 | Jewish revolt | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 68-69 |
|
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 69-79 |
|
 Histories
and treatises of Pliny the Elder Histories
and treatises of Pliny the Elder |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 79-81 |
 Titus Titus |
79 |  Eruption
of Vesuvius Eruption
of Vesuvius |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 81-96 |  Domitian Domitian
 |
80 |
 Colosseum Colosseum |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 96-98 |
 Nerva Nerva
|
Epigrams
of Martial, rhetoric of Quintilian Histories of Tacitus, letters of Pliny the Younger, satires of Juvenal  |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 98-117 |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 107 |  Conquest
of Dacia Conquest
of Dacia |
112 |
 Trajan's
forum Trajan's
forum |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 117-138 |
 Hadrian Hadrian
|
122 |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 138-161 |   Antoninus
Pius Antoninus
Pius |
142 |  Hadrian's
Wall Hadrian's
WallAntonine Wall Novel and oratory of Apuleius; legal writings of Gaius |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 161-180 |
 Marcus
Aurelius Marcus
Aurelius |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 180-192 |
 Commodus Commodus
|
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 193-235 |  Severan
dynasty Severan
dynasty |
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 212 |  Roman
citizenship extended to all free inhabitants of the empire Roman
citizenship extended to all free inhabitants of the empire |
216 |  Baths
of Caracalla Baths
of Caracalla |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 272 |  Dacia
ceded to the Goths Dacia
ceded to the Goths |
260 | Decree of toleration of Christianity | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 284-305 |
 Diocletian Diocletian
|
271 |
 Aurelian's
city wall Aurelian's
city wall |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 293 |  Tetrarchy
established Tetrarchy
established |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 307-337 |  Constantine
I Constantine
I |
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 312 |
|
315 |
 Arch
of Constantine Arch
of Constantine
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 410 |  Britain
told to defend itself Britain
told to defend itself |
324 | Foundation of Constantinople | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 455 | Vandals sack Rome |
  |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 476 | Loss of western Roman empire complete |   |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

 Iron
Age huts on Palatine hill
Iron
Age huts on Palatine hill  Laws
of Gaius Gracchu
Laws
of Gaius Gracchu Speeches,
treatises and letters of Cicero; poetry of Catullus and Lucretius; histories
of Caesar; 55 Pompey's theatre
Speeches,
treatises and letters of Cicero; poetry of Catullus and Lucretius; histories
of Caesar; 55 Pompey's theatre Augustus'
Res Gestae
Augustus'
Res Gestae Galba,
Otho, Vitellius
Galba,
Otho, Vitellius 
 Vespasian
Vespasian
 Trajan
Trajan 
 Biographies
of Suetonius
Biographies
of Suetonius

 Defeat
of Maxentius at Milvian Bridge
Defeat
of Maxentius at Milvian Bridge 



